The Best Way to Avoid Diabetes: What if I told you it was possible to delay or even prevent diabetes? What if I offered a solution that has proven itself over and over again? Would you take my advice?
Americans have a love affair with food. We delight in every crispy fry and whip cream topped desert. We snack on decadent chocolate and love those bacon double cheeseburgers with an extra large soda.
Of course we can justify the indulgence. We work hard. We must manage enormous stress. Food is our coping mechanism of choice.
The problem is that proportionally Americans are getting larger and we’re exporting the fast paced, stress filled and often sedentary lifestyle around the globe. The world is getting bigger and with that growth comes the potential for onset diabetes.
We don’t want it, we certainly don’t want to talk about it and we’ll avoid finding out for sure. If we just push through one more day perhaps the disease will go away thinking we just aren’t interested.
The truth is diabetes will set up house without your permission. It can be hereditary, but it’s often the result of accumulated lifestyle choices.
If your idea of a diet is simply to consume whatever pleases you most you may eventually struggle with the reality of diabetes. If your idea of exercise is a trip from the easy chair to the kitchen or to find the remote you may be setting yourself up for issues related to diabetes.
If you’ll think back to the beginning of this article I mentioned the possibility of delaying or even preventing diabetes if caught early enough. Would you like to know the secret?
If you can adjust your eating habits and exercise routine in order to lose 5%-7% of your total body weight you can slow down the diabetic freight train. Obviously this advice is for those who are overweight or even obese, but it is also a cautionary tale to all who believe a diet based on personal tastes alone is acceptable.
Five percent of your body weight could be less than ten pounds. What that means is a little motivation toward improved personal health care today could result in improved personal health long term.
If this is indeed a case of a runaway train then doesn’t it make sense to try to stop it before it crashes?
I know the choices at a fast food restaurant are enticing, and it’s so convenient to order from a numerical menu and drive away clamping your jaws around a #2 with a fist full of fries, but there might be a similarly convenient way to manage meals on the go with a menu that may be more nutritionally sound.
In most grocery stores or supermarkets you will find a deli with pre-packaged meals. In most cases these meals cost less than take out and may be better nutritionally than fast food. They will probably even taste better.
Take advantage of the salad bars and the pre cut fruit cups. The point is there are ways to make better food choices that facilitate meaningful life changes.
Park a bit further away from the store and walk a bit more. Take your pet for a walk. Take your spouse for a walk. Ride your bike. Visit a community aerobics class. Swim.
Find ways to include activity in your daily routine. It doesn’t have to be an all-day ordeal. A few minutes of activity is worth more than you may realize.
The combination of better food choices and a more active lifestyle will reduce stress, increase energy, reduce weight, and will remain the best alternative to diabetes prevention or delay.
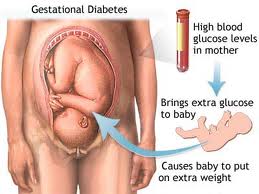 What Is
What Is 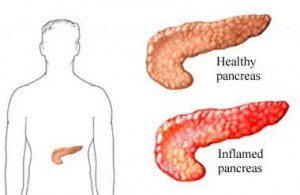 Chronic Pancreatitis: Excellent physical condition is everyone’s golden dream. However, some conditions hinder the realization of this dream. Chronic pancreatitis is one such condition. Constant inflammation of the pancreas leads to irreparable corrosion of the pancreatic structure and function.
Chronic Pancreatitis: Excellent physical condition is everyone’s golden dream. However, some conditions hinder the realization of this dream. Chronic pancreatitis is one such condition. Constant inflammation of the pancreas leads to irreparable corrosion of the pancreatic structure and function. Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT) is a fasting plasma glucose level less than seven mmol/l with a 2-hour oral tolerance test of glucose, at a value of between seven point eight and eleven point one mmol/l. This condition is usually characterized by
Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT) is a fasting plasma glucose level less than seven mmol/l with a 2-hour oral tolerance test of glucose, at a value of between seven point eight and eleven point one mmol/l. This condition is usually characterized by