 Heart Disease And Diabetes: Diabetes is a complicated medical condition that affects the body’s ability to regulate insulin and thus, sugar levels in the body. According to the recent statistics there are over 23 million people in the United States with diabetes. Having diabetes takes a serious toll on the body and puts a person at greater risk for many other serious diseases including heart disease. In fact, a person with diabetes is two times more likely to develop heart disease than someone who does not have the illness. Diabetes in one of the top five causes of death and although it has no “cure,” proper treatment can help a person live a longer healthier life.
Heart Disease And Diabetes: Diabetes is a complicated medical condition that affects the body’s ability to regulate insulin and thus, sugar levels in the body. According to the recent statistics there are over 23 million people in the United States with diabetes. Having diabetes takes a serious toll on the body and puts a person at greater risk for many other serious diseases including heart disease. In fact, a person with diabetes is two times more likely to develop heart disease than someone who does not have the illness. Diabetes in one of the top five causes of death and although it has no “cure,” proper treatment can help a person live a longer healthier life.
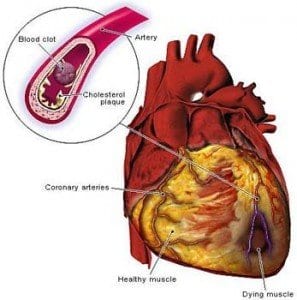
Why does having diabetes increase a person’s risk for heart disease? Researchers discovered a link between the amount of cholesterol in the bloodstream and the occurrence of heart disease many years ago, but how those high cholesterol levels occurred was based on an incorrect assumption. The scientists, doctors and media latched on to the incorrect idea that eating a diet high in cholesterol leads to an increased risk of heart disease. The idea spread like wildfire and the low-fat diet became the standard advice from physicians.
The problem was that there was no evidence linking cholesterol in food to heart disease, it was the blood levels of cholesterol. This is where the connection between heart disease and diabetes comes in. High blood levels of cholesterol occur when there is too much sugar in the blood. The liver can only process a certain amount of sugar at a time and the rest is stored in the body in the form of fat—cholesterol laden body fat. It is also widely understood that increased body fat puts a person at greater risk for heart disease and diabetes sufferers often have increased weight.
So what can be done to prevent heart disease and control diabetes? Fortunately, by taking the same actions that help keep diabetes under control, a person can also help to reduce the risk of heart disease. Losing excess weight, getting regular exercise and eating a healthy, balanced diet that is rich in protein, whole grains and vegetables and low in sugar can greatly improve diabetes control and help to reduce the risk of heart disease. It is also important to see your doctor for regular check-ups and to have your blood tested.